Why Benchmark & Standard are Crucial in Investing?A benchmark serves a crucial role in investing.
A model portfolio may serve as a benchmark to provide a starting point for a portfolio manager to construct a portfolio and directs how that portfolio should be managed on an ongoing basis from the perspectives of both risk and return. It also allows investors to gauge the relative performance of their portfolios.
|
What is a Benchmark?
A benchmark is a standard against which the performance of a security, mutual fund or investment manager can be measured. Generally, broad market and market-segment stock and bond indexes are used for this purpose.
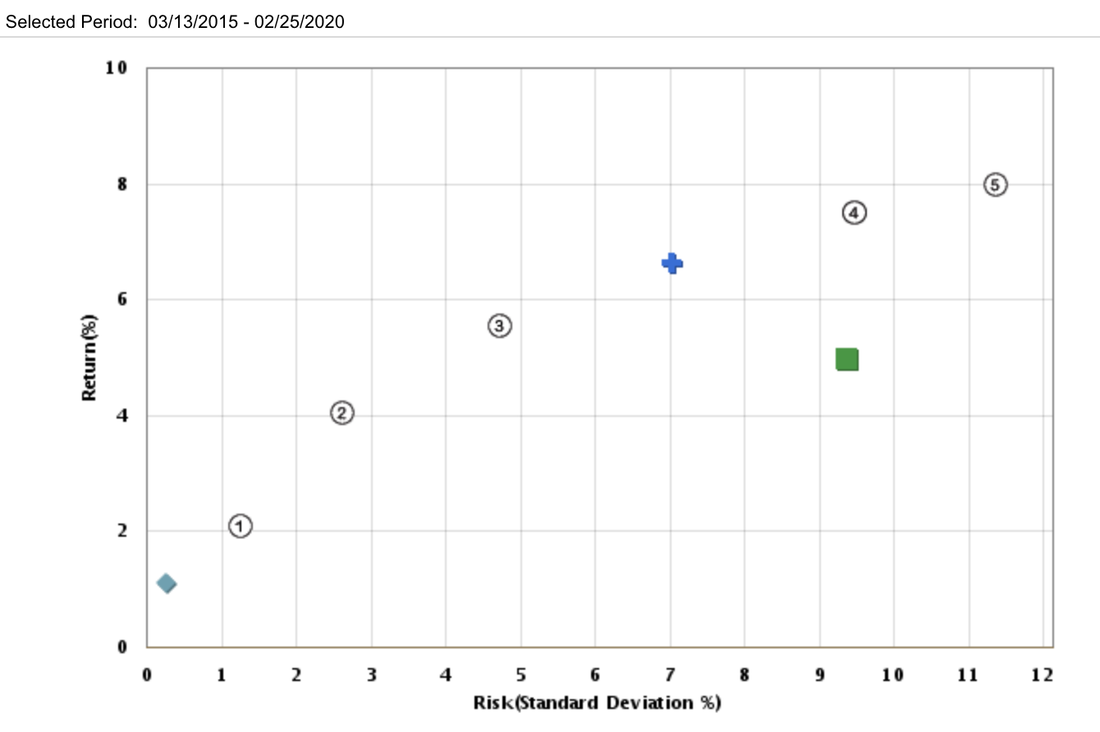
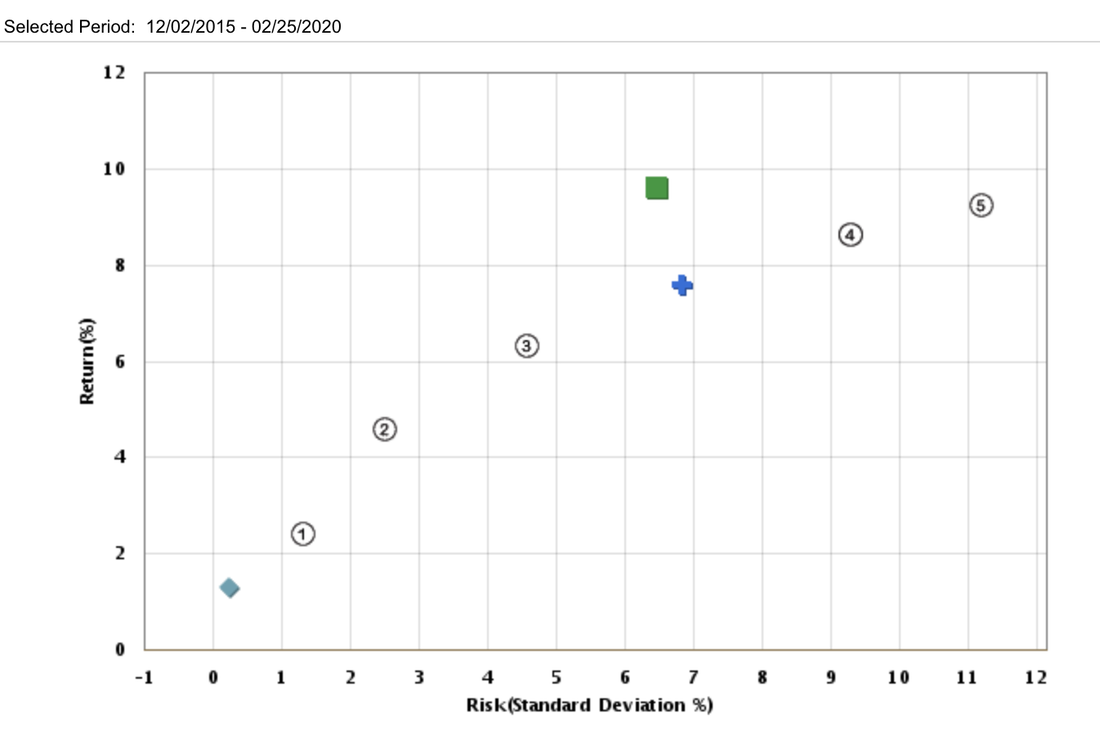
Examples of Performance against Benchmark
Benchmark Standard
Six portfolio benchmarks are defined as the standard to evaluate a portfolio's performance for the given risk tolerance level, ranging from Short-Term, Conservative, Moderate Conservative, Moderate, Moderately Aggressive, to Aggressive.
A portfolio benchmark standard can be created by a combination of multiple well-selected single market indexes. Our intelligent model portfolios adopt a set of popular portfolio benchmarks defined below. For performance illustration, we also include cash (or 3-Month T-Bill) as the baseline benchmark.
① Short Term benchmark: 60% FTSE 3-Month Treasury Bill, 40% Bloomberg Barclays U.S. Aggregate Bond.
② Conservative benchmark: 50% Bloomberg Barclays U.S. Aggregate Bond, 30% FTSE 3-Month Treasury Bill, 15% S&P 500, 5% MSCI EAFE.
③ Moderately Conservative benchmark: 50% Bloomberg Barclays U.S. Aggregate Bond, 25% S&P 500, 10% FTSE 3-Month Treasury Bill, 10% MSCI EAFE, 5% Russell 2000.
④ Moderate benchmark: 35% Bloomberg Barclays U.S. Aggregate Bond, 35% S&P 500, 15% MSCI EAFE, 10% Russell 2000, 5% FTSE 3-Month Treasury Bill.
⑤ Moderately Aggressive benchmark: 45% S&P 500, 20% MSCI EAFE, 15% Bloomberg Barclays U.S. Aggregate Bond, 15% Russell 2000, 5% FTSE 3-Month Treasury Bill.
⑥ Aggressive benchmark: 50% S&P 500, 25% MSCI EAFE, 20% Russell 2000, 5% FTSE 3-Month Treasury Bill.
② Conservative benchmark: 50% Bloomberg Barclays U.S. Aggregate Bond, 30% FTSE 3-Month Treasury Bill, 15% S&P 500, 5% MSCI EAFE.
③ Moderately Conservative benchmark: 50% Bloomberg Barclays U.S. Aggregate Bond, 25% S&P 500, 10% FTSE 3-Month Treasury Bill, 10% MSCI EAFE, 5% Russell 2000.
④ Moderate benchmark: 35% Bloomberg Barclays U.S. Aggregate Bond, 35% S&P 500, 15% MSCI EAFE, 10% Russell 2000, 5% FTSE 3-Month Treasury Bill.
⑤ Moderately Aggressive benchmark: 45% S&P 500, 20% MSCI EAFE, 15% Bloomberg Barclays U.S. Aggregate Bond, 15% Russell 2000, 5% FTSE 3-Month Treasury Bill.
⑥ Aggressive benchmark: 50% S&P 500, 25% MSCI EAFE, 20% Russell 2000, 5% FTSE 3-Month Treasury Bill.
Further Readings
- The CFA Institute Global Investment Performance Standards (GIPS®) are globally accepted standards considered industry best practice for investment performance reporting and presentation. Adopted by hundreds of organizations around the world, the GIPS standards have been implemented by most of the top asset management firms.
- Two other important benchmark performance measures are being used in financial institutions. They are Maximum Drawdown (MDD) and Up/Down Market Capture Ratios. Investors can do a performance benchmark analysis by examining if these two measures found in their portfolio performance report prepared by the financial institution.
- Fidelity target allocation model portfolios are designed to provide enhanced risk-adjusted total return across the risk spectrum. They seeks to enhance total return through fund selection and diversifies across asset classes and sub-asset classes.